机器学习 - 多项式回归
多项式回归
如果您的数据点明显不适合线性回归(穿过所有数据点的直线),那么多项式回归可能就是理想的选择。
多项式回归与线性回归一样,使用变量 x 和 y 之间的关系来找到穿过数据点的最佳直线。
它是如何工作的?
Python 提供了用于查找数据点之间关系和绘制多项式回归线的方法。我们将向您展示如何使用这些方法,而不是深入研究数学公式。
在下面的示例中,我们记录了 18 辆汽车通过某个收费站的情况。
我们记录了汽车的速度,以及通过的时间(小时)。
x 轴表示一天中的小时,y 轴表示速度。
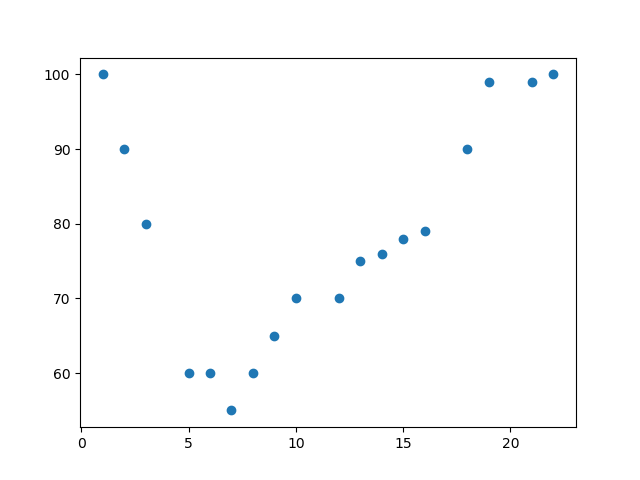
示例
首先绘制散点图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
结果
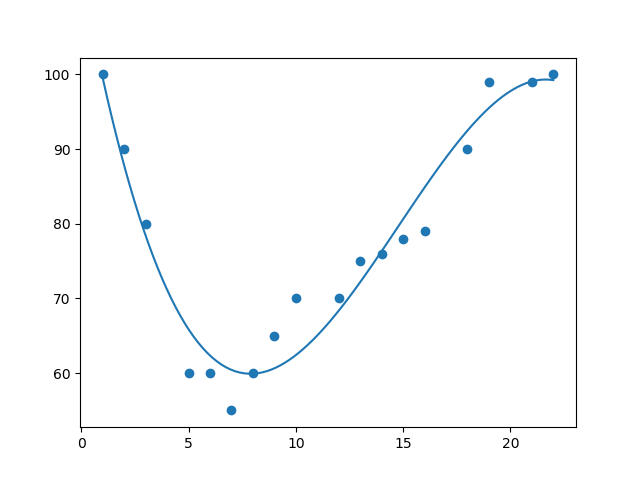
示例
导入 numpy 和 matplotlib,然后绘制多项式回归线
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
myline = numpy.linspace(1, 22, 100)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(myline, mymodel(myline))
plt.show()
结果

示例解释
导入所需的模块。
您可以在我们的 NumPy 教程中了解 NumPy 模块。
您可以在我们的 SciPy 教程中了解 SciPy 模块。
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
创建表示 x 和 y 轴值的数组
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
NumPy 有一个方法可以让我们创建多项式模型
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
然后指定直线的显示方式,我们从位置 1 开始,到位置 22 结束
myline = numpy.linspace(1, 22, 100)
绘制原始散点图
plt.scatter(x, y)
绘制多项式回归线
plt.plot(myline, mymodel(myline))
显示图表
plt.show()
R-平方
了解 x 轴和 y 轴变量之间的关系有多好很重要,如果没有关系,多项式回归就无法用于任何预测。
这种关系用一个称为 r-squared 的值来衡量。
r-squared 值范围从 0 到 1,其中 0 表示没有关系,1 表示 100% 相关。
Python 和 Sklearn 模块可以为您计算此值,您只需将 x 和 y 数组输入其中即可
示例
我的数据在多项式回归中的拟合度如何?
import numpy
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
print(r2_score(y, mymodel(x)))
亲自尝试 »
注意:结果 0.94 表明存在非常好的关系,我们可以将多项式回归用于未来的预测。
预测未来值
现在我们可以利用收集到的信息来预测未来值。
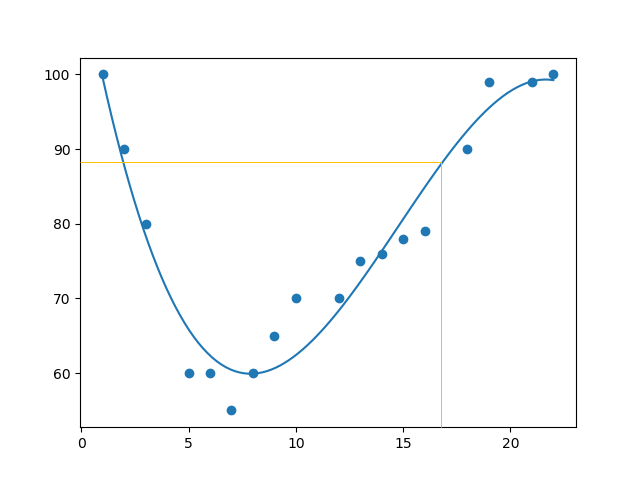
示例:让我们尝试预测一辆在 17:00 左右通过收费站的汽车的速度。
为此,我们需要上面示例中的相同 mymodel 数组
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
示例
预测 17:00 通过的汽车的速度
import numpy
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
x = [1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,21,22]
y = [100,90,80,60,60,55,60,65,70,70,75,76,78,79,90,99,99,100]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
speed = mymodel(17)
print(speed)
运行示例 »
该示例预测的速度为 88.87,我们也可以从图表中读出这个值。
拟合不佳?
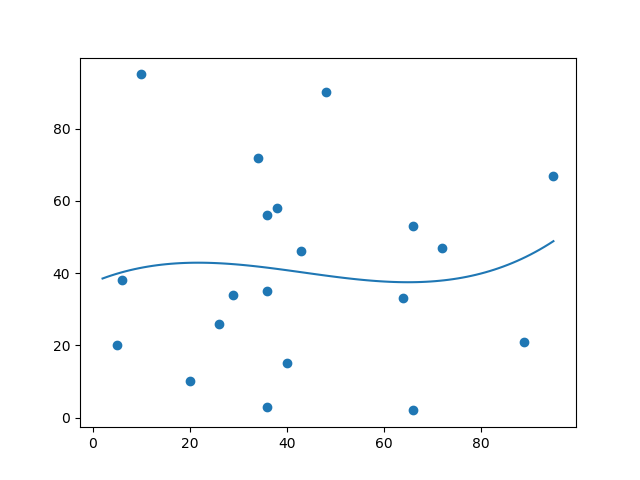
让我们创建一个多项式回归不适合用于预测未来值的示例。
示例
这些 x 轴和 y 轴的值对于多项式回归来说应该拟合得很差。
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [89,43,36,36,95,10,66,34,38,20,26,29,48,64,6,5,36,66,72,40]
y = [21,46,3,35,67,95,53,72,58,10,26,34,90,33,38,20,56,2,47,15]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
myline = numpy.linspace(2, 95, 100)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(myline, mymodel(myline))
plt.show()
结果
那么 r-squared 值是多少?
示例
您应该得到一个非常低的 r-squared 值。
import numpy
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
x = [89,43,36,36,95,10,66,34,38,20,26,29,48,64,6,5,36,66,72,40]
y = [21,46,3,35,67,95,53,72,58,10,26,34,90,33,38,20,56,2,47,15]
mymodel = numpy.poly1d(numpy.polyfit(x, y, 3))
print(r2_score(y, mymodel(x)))
亲自尝试 »
结果:0.00995 表明关系非常糟糕,并且告诉我们该数据集不适合多项式回归。

