机器学习 - K-means
在此页面上,W3schools.com 与 纽约数据科学学院 合作,为我们的学生提供数字培训内容。
K-means
K-means 是一种用于对数据点进行聚类的无监督学习方法。该算法通过最小化每个簇内的方差来迭代地将数据点划分为 K 个簇。
在此,我们将向您展示如何使用肘部方法估算 K 的最佳值,然后使用 K-means 聚类将数据点分组到簇中。
它是如何工作的?
首先,每个数据点被随机分配到 K 个簇中的一个。然后,我们计算每个簇的质心(实质上是中心),并将每个数据点重新分配到距离质心最近的簇。我们重复此过程,直到每个数据点的簇分配不再发生变化为止。
K-means 聚类要求我们选择 K,即我们想要将数据分组成的簇的数量。肘部方法可以让我们绘制惯性(一种基于距离的度量)图,并可视化其开始线性下降的点。这个点被称为“肘部”,是基于我们数据选择 K 最佳值的良好估计。
示例
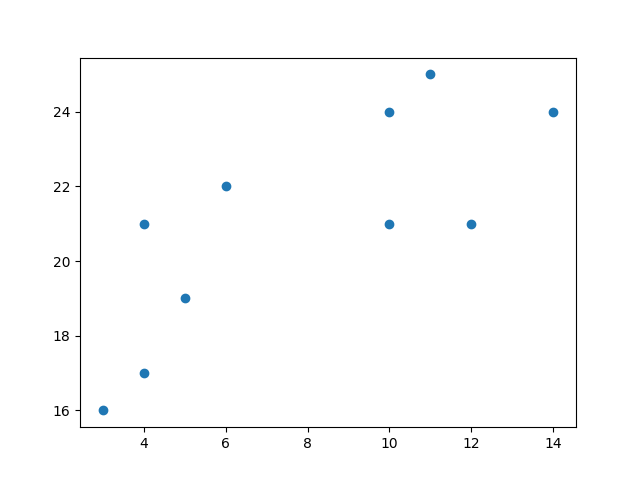
首先,可视化一些数据点
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [4, 5, 10, 4, 3, 11, 14 , 6, 10, 12]
y = [21, 19, 24, 17, 16, 25, 24, 22, 21, 21]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
结果
广告
现在我们使用肘部方法来可视化不同 K 值的惯性
示例
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
data = list(zip(x, y))
inertias = []
for i in range(1,11)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=i)
kmeans.fit(data)
inertias.append(kmeans.inertia_)
plt.plot(range(1,11), inertias, marker='o')
plt.title('肘部方法')
plt.xlabel('簇的数量')
plt.ylabel('惯性')
plt.show()
结果
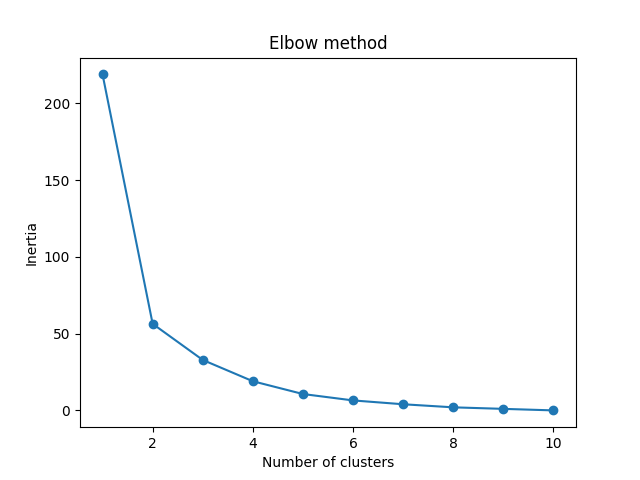
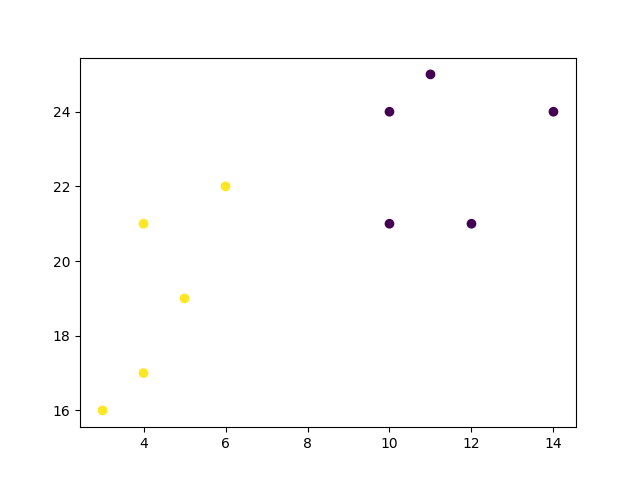
肘部方法显示 2 是 K 的一个好值,因此我们重新训练并可视化结果
示例
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2)
kmeans.fit(data)
plt.scatter(x, y, c=kmeans.labels_)
plt.show()
结果
示例解释
导入所需的模块。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
你可以在我们的 “Matplotlib 教程”中了解 Matplotlib 模块。
scikit-learn 是一个流行的机器学习库。
创建类似于数据集中两个变量的数组。请注意,虽然这里我们只使用了两个变量,但这种方法适用于任何数量的变量。
x = [4, 5, 10, 4, 3, 11, 14 , 6, 10, 12]
y = [21, 19, 24, 17, 16, 25, 24, 22, 21, 21]
将数据转换为一组点
data = list(zip(x, y))
print(data)
结果
[(4, 21), (5, 19), (10, 24), (4, 17), (3, 16), (11, 25), (14, 24), (6, 22), (10, 21), (12, 21)]
为了找到 K 的最佳值,我们需要在一定范围内运行 K-means 对我们的数据进行处理。我们只有 10 个数据点,所以最多可以有 10 个簇。因此,对于 range(1,11) 中的每个 K 值,我们训练一个 K-means 模型,并绘制该簇数量下的惯性。
inertias = []
for i in range(1,11)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=i)
kmeans.fit(data)
inertias.append(kmeans.inertia_)
plt.plot(range(1,11), inertias, marker='o')
plt.title('肘部方法')
plt.xlabel('簇的数量')
plt.ylabel('惯性')
plt.show()
结果

我们可以看到,上面图中的“肘部”(惯性变得更线性的地方)在 K=2。然后,我们可以再拟合一次 K-means 算法,并绘制分配给数据的不同簇。
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2)
kmeans.fit(data)
plt.scatter(x, y, c=kmeans.labels_)
plt.show()
结果


