机器学习 - 线性回归
回归
当您尝试找出变量之间的关系时,使用术语“回归”。
在机器学习和统计建模中,这种关系被用来预测未来事件的结果。
线性回归
线性回归利用数据点之间的关系来绘制一条穿过所有数据点的直线。
这条线可用于预测未来值。
在机器学习中,预测未来非常重要。
它是如何工作的?
Python 提供了查找数据点之间关系并绘制线性回归线的方法。我们将向您展示如何使用这些方法,而不是通过数学公式。
在下面的示例中,x 轴代表年龄,y 轴代表速度。我们记录了 13 辆汽车通过收费站时的年龄和速度。让我们看看收集到的数据是否可以用于线性回归。
示例
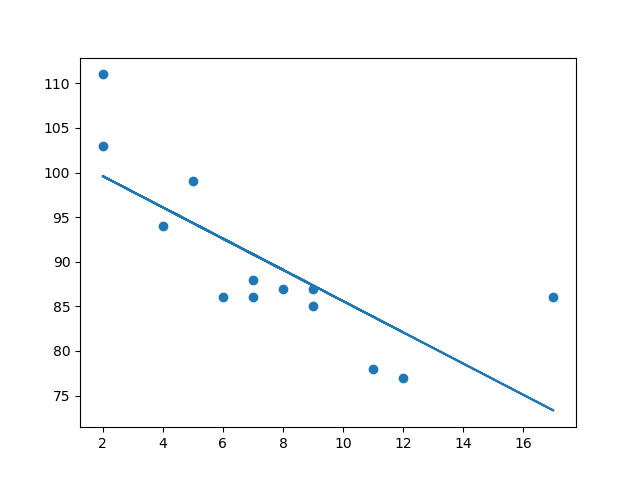
首先绘制散点图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [5,7,8,7,2,17,2,9,4,11,12,9,6]
y = [99,86,87,88,111,86,103,87,94,78,77,85,86]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
结果
示例
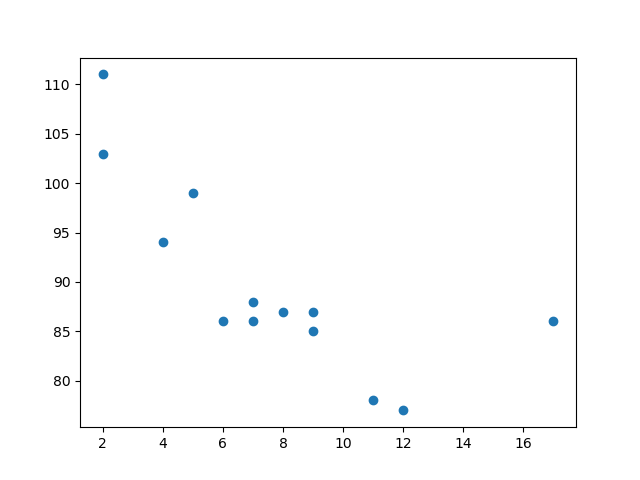
导入 scipy 并绘制线性回归线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
x = [5,7,8,7,2,17,2,9,4,11,12,9,6]
y = [99,86,87,88,111,86,103,87,94,78,77,85,86]
slope, intercept, r, p, std_err = stats.linregress(x, y)
def myfunc(x)
return slope * x + intercept
mymodel = list(map(myfunc, x))
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, mymodel)
plt.show()
结果

示例解释
导入所需的模块。
您可以在我们的 Matplotlib 教程 中了解 Matplotlib 模块。
您可以在我们的 SciPy 教程 中了解 SciPy 模块。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
创建代表 x 轴和 y 轴值的数组
x = [5,7,8,7,2,17,2,9,4,11,12,9,6]
y = [99,86,87,88,111,86,103,87,94,78,77,85,86]
执行一个返回线性回归一些重要关键值的函数
slope, intercept, r, p, std_err = stats.linregress(x, y)
创建一个函数,该函数使用 slope 和 intercept 值来返回一个新值。这个新值表示对应 x 值的 y 轴位置
def myfunc(x)
return slope * x + intercept
将 x 数组的每个值通过函数运行。这将生成一个包含新 y 轴值的新数组
mymodel = list(map(myfunc, x))
绘制原始散点图
plt.scatter(x, y)
绘制线性回归线
plt.plot(x, mymodel)
显示图表
plt.show()
R 代表相关性
了解 x 轴值和 y 轴值之间的关系很重要。如果没有关系,线性回归就不能用于预测任何内容。
这种关系——相关系数——称为 r。
r 值范围从 -1 到 1,其中 0 表示无关系,1(和 -1)表示 100% 相关。
Python 和 Scipy 模块会为您计算此值,您只需将 x 和 y 值输入即可。
示例
我的数据与线性回归的拟合程度如何?
from scipy import stats
x = [5,7,8,7,2,17,2,9,4,11,12,9,6]
y = [99,86,87,88,111,86,103,87,94,78,77,85,86]
slope, intercept, r, p, std_err = stats.linregress(x, y)
print(r)
自己动手试一试 »
注意:结果 -0.76 表明存在关系,虽然不完美,但表明我们可以将线性回归用于未来的预测。
预测未来值
现在我们可以利用收集到的信息来预测未来值。
示例:让我们尝试预测一辆 10 年车龄汽车的速度。
为此,我们需要上面示例中的相同 myfunc() 函数
def myfunc(x)
return slope * x + intercept
示例
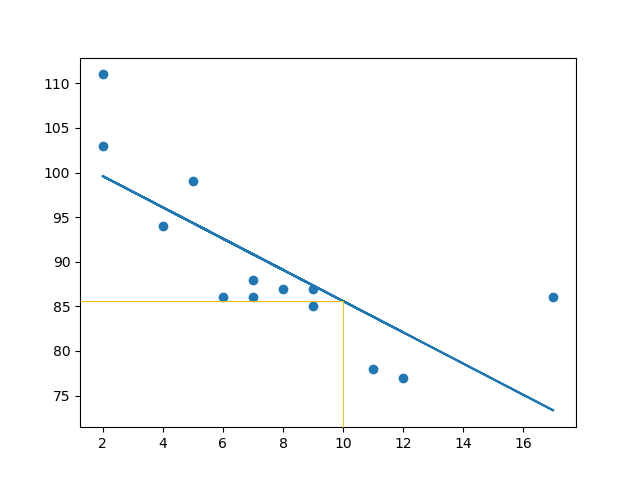
预测一辆 10 年车龄汽车的速度
from scipy import stats
x = [5,7,8,7,2,17,2,9,4,11,12,9,6]
y = [99,86,87,88,111,86,103,87,94,78,77,85,86]
slope, intercept, r, p, std_err = stats.linregress(x, y)
def myfunc(x)
return slope * x + intercept
speed = myfunc(10)
print(speed)
运行示例 »
示例预测速度为 85.6,我们也可以从图表中读出该值。
拟合效果差?
让我们举一个线性回归不是预测未来值的最佳方法的例子。
示例
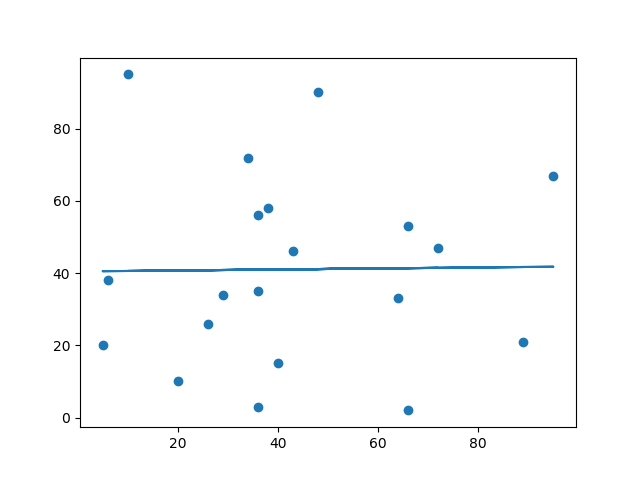
这些 x 轴和 y 轴的值应该会导致线性回归的拟合效果非常差。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
x = [89,43,36,36,95,10,66,34,38,20,26,29,48,64,6,5,36,66,72,40]
y = [21,46,3,35,67,95,53,72,58,10,26,34,90,33,38,20,56,2,47,15]
slope, intercept, r, p, std_err = stats.linregress(x, y)
def myfunc(x)
return slope * x + intercept
mymodel = list(map(myfunc, x))
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, mymodel)
plt.show()
结果
以及 r 的关系如何?
示例
您应该得到一个非常低的 r 值。
import numpy
from scipy import stats
x = [89,43,36,36,95,10,66,34,38,20,26,29,48,64,6,5,36,66,72,40]
y = [21,46,3,35,67,95,53,72,58,10,26,34,90,33,38,20,56,2,47,15]
slope, intercept, r, p, std_err = stats.linregress(x, y)
print(r)
自己动手试一试 »
结果:0.013 表明关系非常差,并告诉我们此数据集不适合进行线性回归。

