机器学习 - 层次聚类
在此页面上,W3schools.com 与 纽约数据科学学院 合作,为我们的学生提供数字培训内容。
层次聚类
层次聚类是一种无监督学习方法,用于对数据点进行聚类。该算法通过测量数据点之间的不相似性来构建簇。无监督学习意味着模型无需训练,我们也不需要“目标”变量。这种方法可用于任何数据,以可视化和解释单个数据点之间的关系。
在这里,我们将使用层次聚类对数据点进行分组,并通过树状图和散点图来可视化这些簇。
它是如何工作的?
我们将使用凝聚聚类,这是一种层次聚类方法,遵循自下而上的方法。我们从将每个数据点视为一个单独的簇开始。然后,我们将距离最短的簇连接起来,形成更大的簇。重复此步骤,直到形成一个包含所有数据点的大簇。
层次聚类要求我们同时确定距离和连接方法。我们将使用欧几里得距离和 Ward 连接方法,该方法试图最小化簇之间的方差。
示例
首先,可视化一些数据点
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [4, 5, 10, 4, 3, 11, 14 , 6, 10, 12]
y = [21, 19, 24, 17, 16, 25, 24, 22, 21, 21]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
结果
广告
现在,我们使用欧几里得距离计算 Ward 连接,并使用树状图进行可视化。
示例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import dendrogram, linkage
x = [4, 5, 10, 4, 3, 11, 14 , 6, 10, 12]
y = [21, 19, 24, 17, 16, 25, 24, 22, 21, 21]
data = list(zip(x, y))
linkage_data = linkage(data, method='ward', metric='euclidean')
dendrogram(linkage_data)
plt.show()
结果

示例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering
x = [4, 5, 10, 4, 3, 11, 14 , 6, 10, 12]
y = [21, 19, 24, 17, 16, 25, 24, 22, 21, 21]
data = list(zip(x, y))
hierarchical_cluster = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2, affinity='euclidean', linkage='ward')
labels = hierarchical_cluster.fit_predict(data)
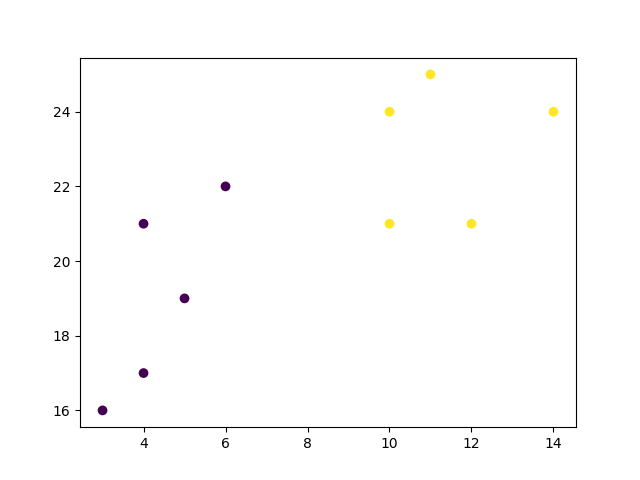
plt.scatter(x, y, c=labels)
plt.show()
结果
示例解释
导入所需的模块。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import dendrogram, linkage
from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering
你可以在我们的 “Matplotlib 教程”中了解 Matplotlib 模块。
您可以在我们的 SciPy 教程 中了解 SciPy 模块。
NumPy 是一个用于在 Python 中处理数组和矩阵的库,您可以在我们的 NumPy 教程 中了解 NumPy 模块。
scikit-learn 是一个流行的机器学习库。
创建类似于数据集中两个变量的数组。请注意,虽然这里我们只使用了两个变量,但此方法适用于任何数量的变量。
x = [4, 5, 10, 4, 3, 11, 14 , 6, 10, 12]
y = [21, 19, 24, 17, 16, 25, 24, 22, 21, 21]
将数据转换为一组点。
data = list(zip(x, y))
print(data)
结果
[(4, 21), (5, 19), (10, 24), (4, 17), (3, 16), (11, 25), (14, 24), (6, 22), (10, 21), (12, 21)]
计算所有不同点之间的连接。这里我们使用简单的欧几里得距离度量和 Ward 连接,它试图最小化簇之间的方差。
linkage_data = linkage(data, method='ward', metric='euclidean')
最后,在树状图中绘制结果。此图将向我们展示从底部(单个点)到顶部(包含所有数据点的一个簇)的簇的层次结构。
plt.show() 允许我们可视化树状图,而不仅仅是原始的连接数据。
dendrogram(linkage_data)
plt.show()
结果

scikit-learn 库允许我们以不同的方式使用层次聚类。首先,我们使用相同的欧几里得距离和 Ward 连接初始化 AgglomerativeClustering 类,并指定 2 个簇。
hierarchical_cluster = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2, affinity='euclidean', linkage='ward')
可以对我们的数据调用 .fit_predict 方法,以使用针对我们选择的簇数量定义的参数来计算簇。
labels = hierarchical_cluster.fit_predict(data) print(labels)
结果
[0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1]
最后,如果我们绘制相同的数据并使用层次聚类方法为每个索引分配的标签来着色点,我们可以看到每个点所属的簇。
plt.scatter(x, y, c=labels)
plt.show()
结果


