SQL INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN 关键字会选择两个表中都具有匹配值的记录。
让我们看看 Products 表的一部分
| ProductID | ProductName | CategoryID | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chais | 1 | 18 |
| 2 | Chang | 1 | 19 |
| 3 | Aniseed Syrup | 2 | 10 |
以及 Categories 表的一部分
| CategoryID | CategoryName | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beverages | Soft drinks, coffees, teas, beers, and ales |
| 2 | Condiments | Sweet and savory sauces, relishes, spreads, and seasonings |
| 3 | Confections | Desserts, candies, and sweet breads |
我们将通过两个表中的 CategoryID 字段,将 Products 表与 Categories 表连接起来。
示例
使用 INNER JOIN 关键字连接 Products 和 Categories 表
SELECT ProductID, ProductName, CategoryName
FROM Products
INNER JOIN Categories ON Products.CategoryID = Categories.CategoryID;
自己动手试一试 »
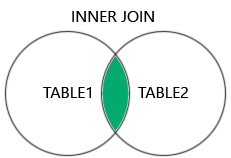
注意: INNER JOIN 关键字只返回两个表中都有匹配的行。这意味着,如果您有一个没有 CategoryID 的产品,或者有一个 CategoryID 不存在于 Categories 表中的产品,那么该记录将不会在结果中返回。
语法
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
命名列
在 SQL 语句中指定列时,包含表名是一个好习惯。
示例
指定表名
SELECT Products.ProductID, Products.ProductName, Categories.CategoryName
FROM Products
INNER JOIN Categories ON Products.CategoryID = Categories.CategoryID;
自己动手试一试 »
上面的例子在不指定表名的情况下也可以工作,因为指定的列名都不存在于两个表中。如果您尝试在 SELECT 语句中包含 CategoryID,而没有指定表名,您将收到一个错误(因为 CategoryID 存在于两个表中)。
JOIN 或 INNER JOIN
JOIN 和 INNER JOIN 会返回相同的结果。
INNER 是 JOIN 的默认连接类型,所以当您写 JOIN 时,解析器实际上会将其写为 INNER JOIN。
示例
JOIN 等同于 INNER JOIN
SELECT Products.ProductID, Products.ProductName, Categories.CategoryName
FROM Products
JOIN Categories ON Products.CategoryID = Categories.CategoryID;
自己动手试一试 »
连接三个表
以下 SQL 语句选择包含客户和发货人信息的订单。
这是 Shippers 表
| ShipperID | ShipperName | Phone |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Speedy Express | (503) 555-9831 |
| 2 | United Package | (503) 555-3199 |
| 3 | Federal Shipping | (503) 555-9931 |
示例
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Shippers.ShipperName
FROM ((Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID)
INNER JOIN Shippers ON Orders.ShipperID = Shippers.ShipperID);
自己动手试一试 »

